Saturday, December 29, 2007
IDIOPATATHIC CYSTITIS CAT URINARY INFECTIONS
Posted by
THE ALLEY CAT FORUM
at
12:42 AM
![]()
Labels: CAT, CAT DISEASES, CAT DISORDERS, CAT HEALTH, CAT URINARY INFECTION, CAT URINARY PROBLEMS, CAT URINARY TRACT, CAT VETERINARIANS, CYSTITIS, MALE CAT URINARY BLOCKAGE, VETERINARIAN
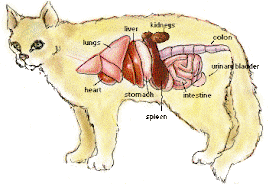
FELINE INFECTIOUS PERITONITIS FIP
Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) is a disease caused by a coronavirus infection. Many different strains of coronavirus are capable of infecting cats, but most do not produce serious disease. FIP-producing strains are distinguished by their ability to invade and grow in certain white blood cells. The infected cells transport the virus throughout the cat's body. An intense inflammatory reaction occurs in the tissues where these virus-infected cells locate. It is this interaction between the body's own immune system and the virus that is responsible for the disease.
Infected cats shed coronavirus in their saliva and feces. Most cats become infected by inhaling or ingesting the virus, either by direct contact with an infected cat, or by contact with virus-contaminated surfaces like clothing, bedding, feeding bowls, or toys.
Although the virus can survive for a number of weeks in the environment, it is rapidly inactivated by most household detergents and disinfectants. An inexpensive and effective disinfectant is one part of household bleach in thirty-two parts of water (4 ounces of bleach per gallon of water). READ MORE HERE:http://www.vet.cornell.edu/fhc/brochures/fip.html
Posted by
THE ALLEY CAT FORUM
at
12:34 AM
![]()
Labels: CAT, CAT DISEASES, CAT HEALTH, CAT VETERINARIANS, FELINE DISORDERS, SICK CAT, VETERINARIAN



















 Custom
Custom 

