Here are some normal behaviors for each cat life stage:
Birth to 16 weeks
Just learning her way around, your kitten may be playful, but most likely shy. Click here for more information on how to care for your new kitten.
16 weeks to 1 year
Your kitten will likely still be very playful and spunky. At approximately six months old, you should spay or neuter if you are not planning to breed your cat.
1 to 8 years
Your young cat is in her prime. Remember your annual visits to the veterinarian.
8 to 12 years
Your pre-geriatric cat may begin to slow down, but her behavior shouldn't change much.
12+ years
Your cat is entering old age. You may begin to notice some health problems. Your cat will move slower if her joints begin to stiffen. She may also become easily irritated.
Final Thought
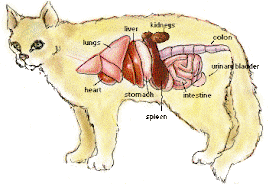
In any health-related issue, whenever you have concerns about your cat, consult your veterinarian. He or she is familiar with your cat and her medical history and has the professional skill and knowledge to identify and treat whatever might be the problem.
Tuesday, October 9, 2007
BEHAVIOR STAGES OF A CATS LIFE
Posted by
THE ALLEY CAT FORUM
at
9:01 PM
![]()
Labels: AGE, BEHAVIOR PROBLEMS, CAT, CAT HEALTH, CAT YEARS, FELINE
WHY SPAY / NEUTER YOUR CAT
Spaying or neutering your cat prevents unwanted births and reduces the influence of sex hormones on your pet's behavior. In seven years, an unspayed female and unneutered male cat can produce up to 781,250 kittens. Homes cannot be found for most of these animals and many either end up in shelters or on the street. Only a lucky few are adopted; the rest are either euthanized or die from trauma, exposure, starvation or disease. By spaying or neutering your cat, you do your part to prevent this tragedy.
Behavior problems can also be prevented or minimized by spaying or neutering your cat. Sexual behavior in both male and female cats is reduced following surgery. In 90% of male cats, neutering eliminated roaming, urine spraying, and fights with neighborhood cats, regardless of their age when neutered. Female cats no longer show "heat" behavior (soliciting mounting from males). Overall, being sexually intact increases the risk of relinquishment to a shelter. There are, however, large individual differences and not all cats undergo a behavior change following spaying or neutering.
Posted by
THE ALLEY CAT FORUM
at
8:56 PM
![]()
Labels: CAT, CAT HEALTH, FELINE, FLEA, NEUTER, SPAY, VETERINARIAN


















 Custom
Custom 

